LESSON 2
Parts of a 3D Printer
In this unit we will cover the basic parts of a 3D printer. We start with 3D Printing components before diving into the mechanical systems that facilitate the printing process.
Extruder
In order to 3D print an object, we need a method of depositing material. The Buildini™ 3D Printer uses a filament extruder to pull plastic into a heated nozzle, liquefy the polymer, and push it out through the nozzle to produce a controlled stream of material.
 Plastic filament extruded from Buildini™ nozzle.
Plastic filament extruded from Buildini™ nozzle.
The extruder consists of two main parts: 1) A Feeding Mechanism to pull in the plastic, and 2) A Hot End to melt and extrude the plastic.
The Feeding Mechanism uses a clamp to grip the filament and a moving gear to pull it into the extruder. The clamp’s grip can be adjusted using the tensioning dial on the left side of the extruder.
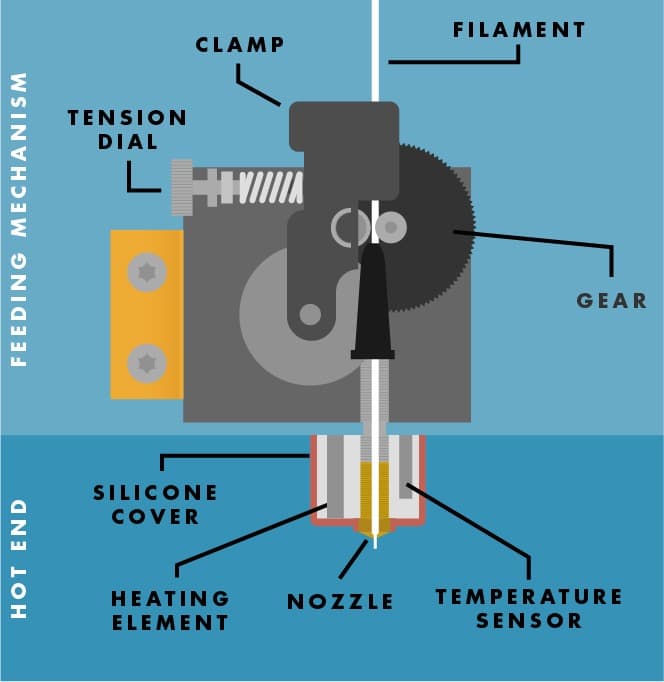 Cut away diagram of the Buildini™ Extruder
Cut away diagram of the Buildini™ Extruder
The Hot End has a heating element to melt the plastic, a temperature sensor to monitor the heat, a nozzle for precise placement of the liquid plastic, and a silicone cover to contain the heat.
Build Platform
Now that we have a extrusion method, we need somewhere for the material to be deposited. That would be the build platform, also called build plate or bed. This is the surface where an object is 3D printed.
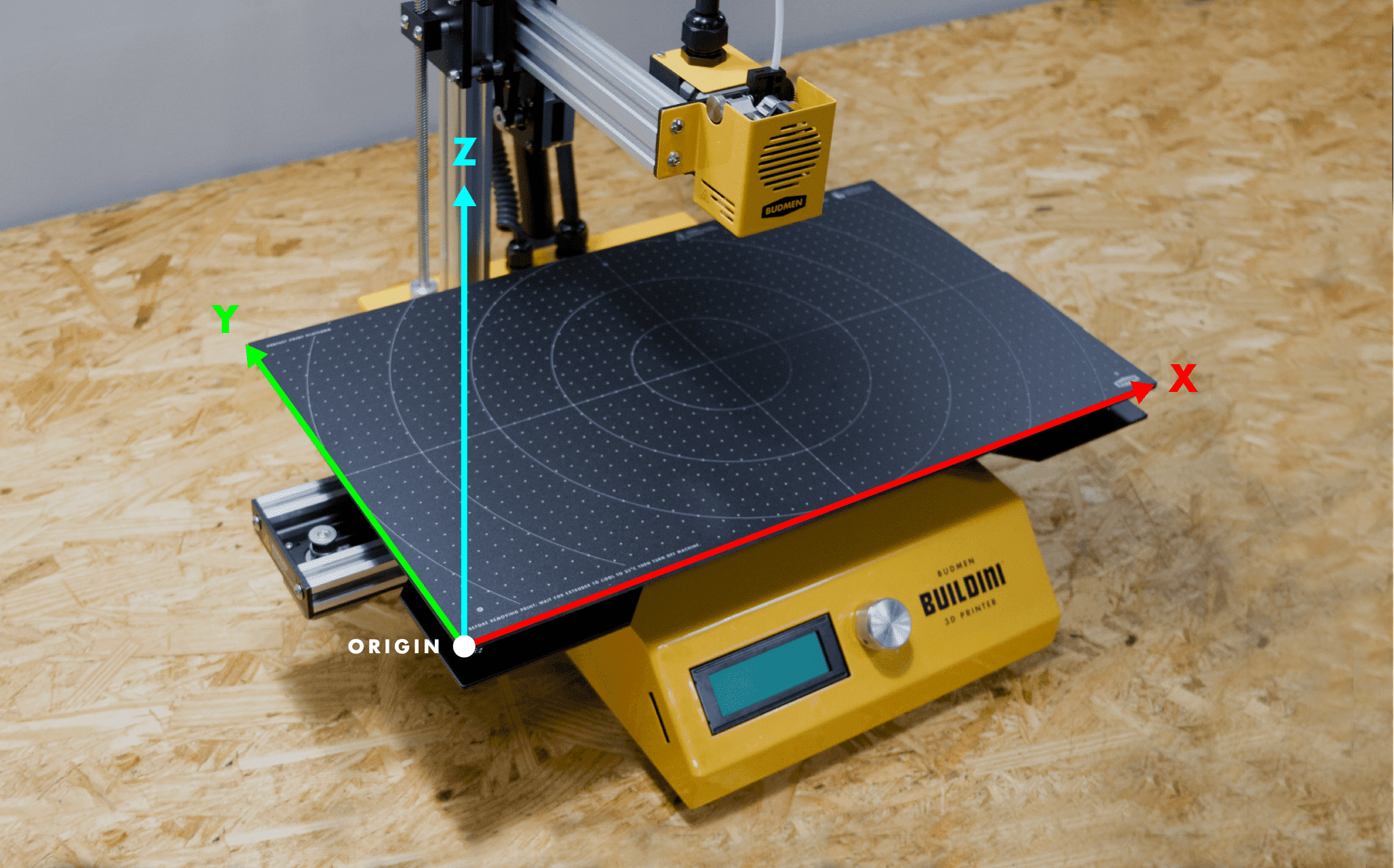 Buildplate with origin or home point marked.
Buildplate with origin or home point marked.
The build platform needs to be level relative to the extruder so the object can be built on a flat surface. This is achieved using three leveling knobs found under the platform. Tightening or loosening these knobs will respectively raise and lower the build platform.
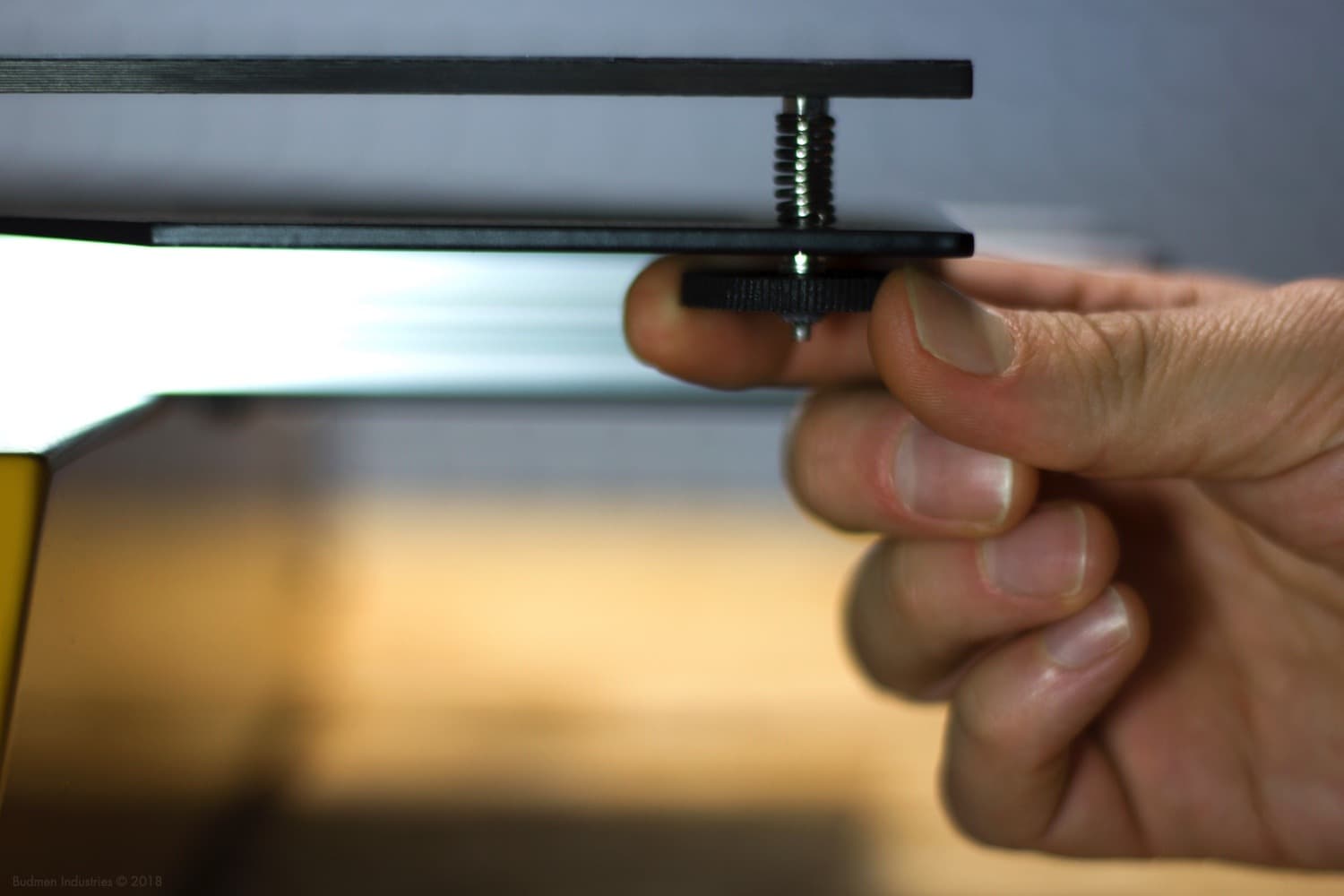 Demonstration of a leveling knob
Demonstration of a leveling knob
Filament + Spool Holder
Filament is a threadlike plastic used by the Buildini™ 3D printer to print objects. The filament spool is placed on the Printer's Spool Holder Arm. The filament is then threaded down the white Teflon tube and into the extruder.
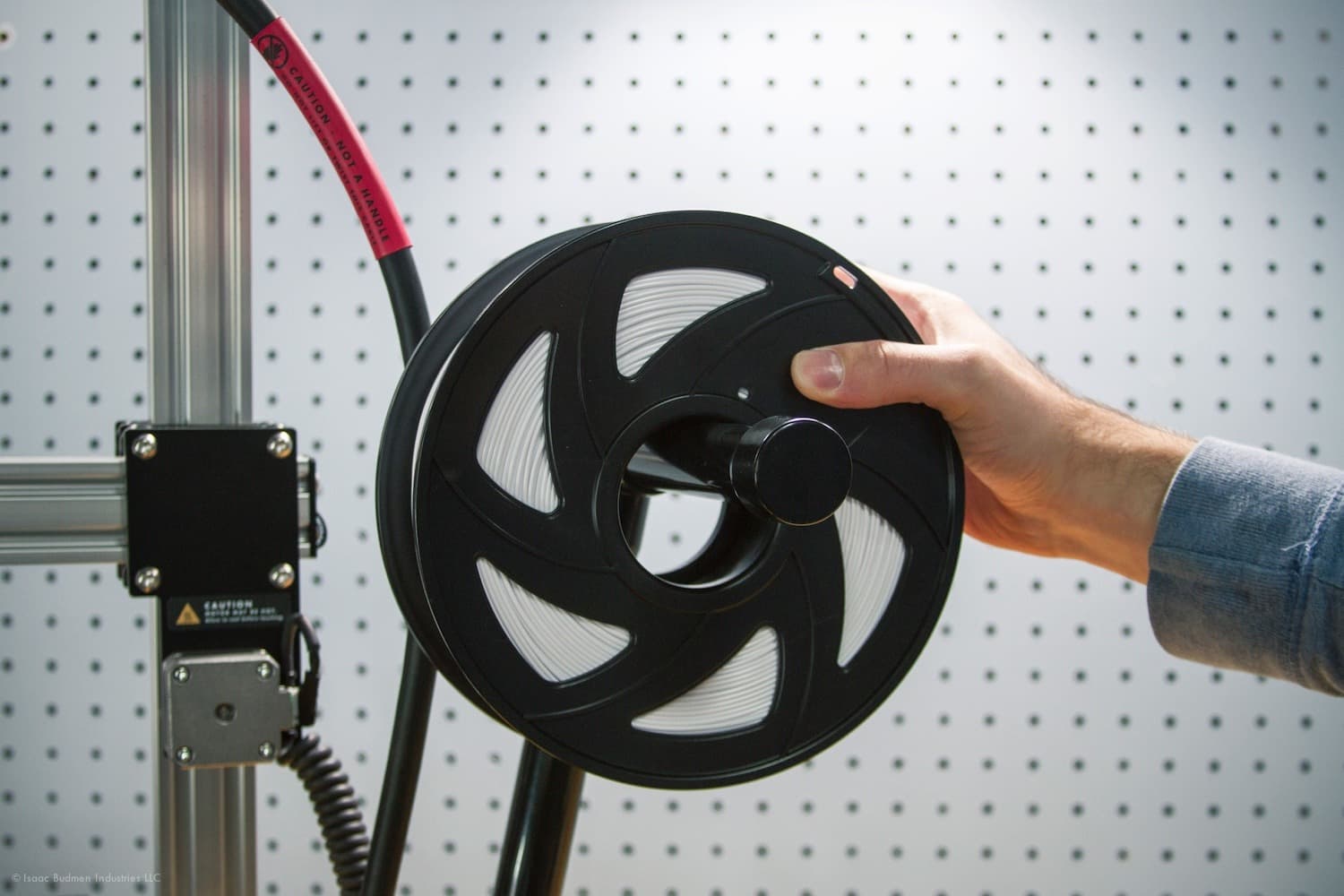 Example of spool of filament placed on Buildini™ spool holder
Example of spool of filament placed on Buildini™ spool holder
Motion System
In order to print in three dimensions, our object needs to be built in three directions: left to right on the build plate on the X-Axis, front to back on the Y-Axis, and up and down on the Z-Axis.
X-Axis
 A demonstration of the X-Axis range of motion.
A demonstration of the X-Axis range of motion.
The first dimension on the Buildini™ 3D Printer is the X-Axis. The motion along the X-Axis is achieved as the build platform rides from side to side along the X-Axis rails. As the X-Axis moves right to left, the plastic is deposited on the build platform in that direction.
Y-Axis
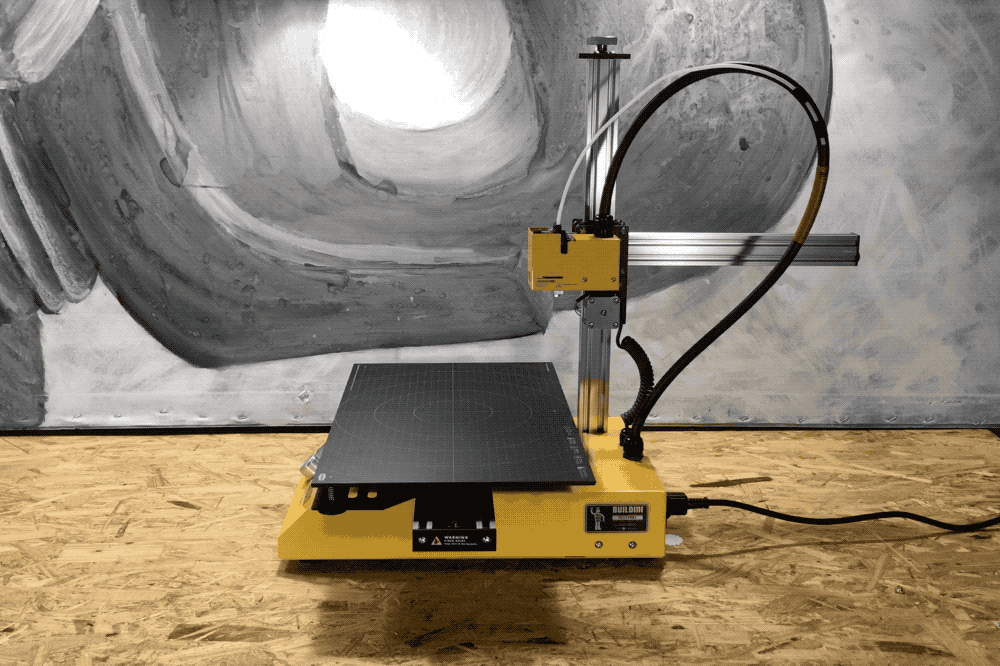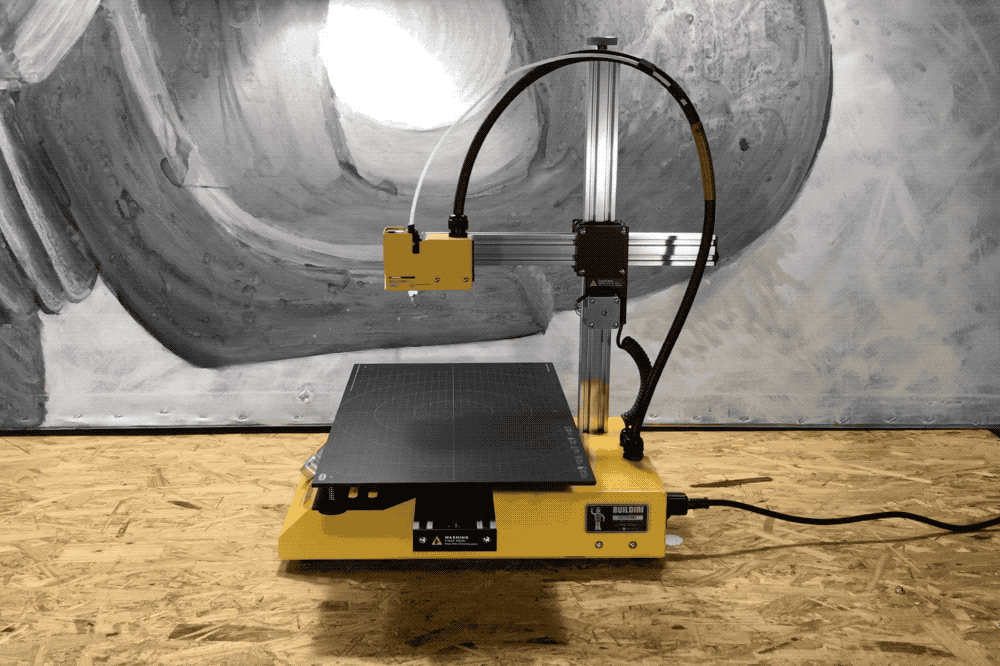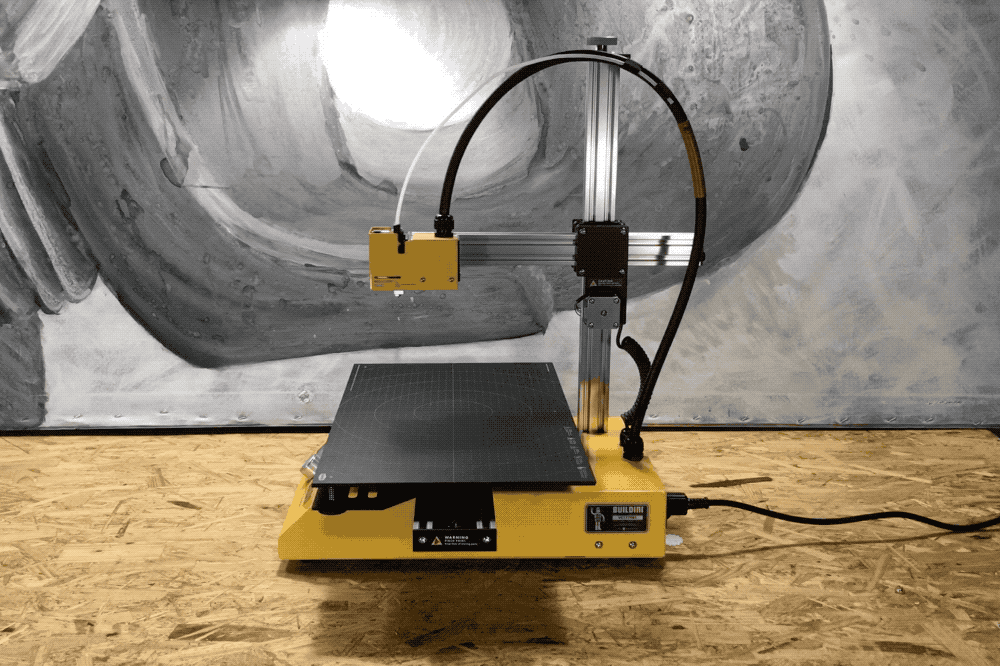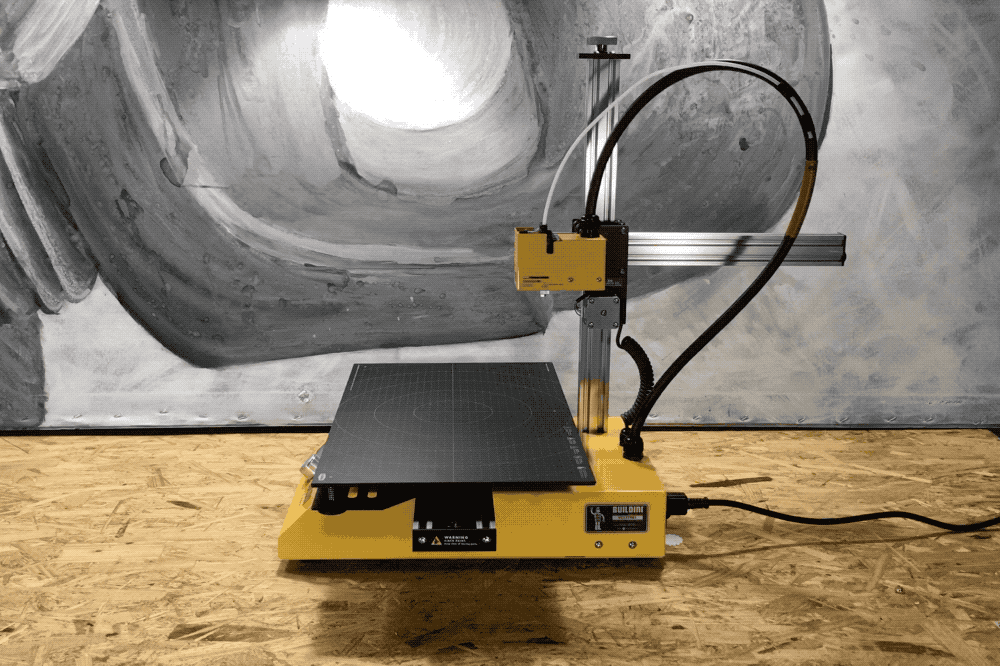 A demonstration of the Y-Axis range of motion.
A demonstration of the Y-Axis range of motion.
The second dimension on the Buildini™ 3D Printer is the Y-Axis. The motion along the Y-Axis creates the front to back motion of the extruder relative to the build platform. The extruder is attached at one end of the Y-Axis. As the Y-Axis moves forward and backward, the plastic is deposited on the build platform in that direction.
Z-Axis
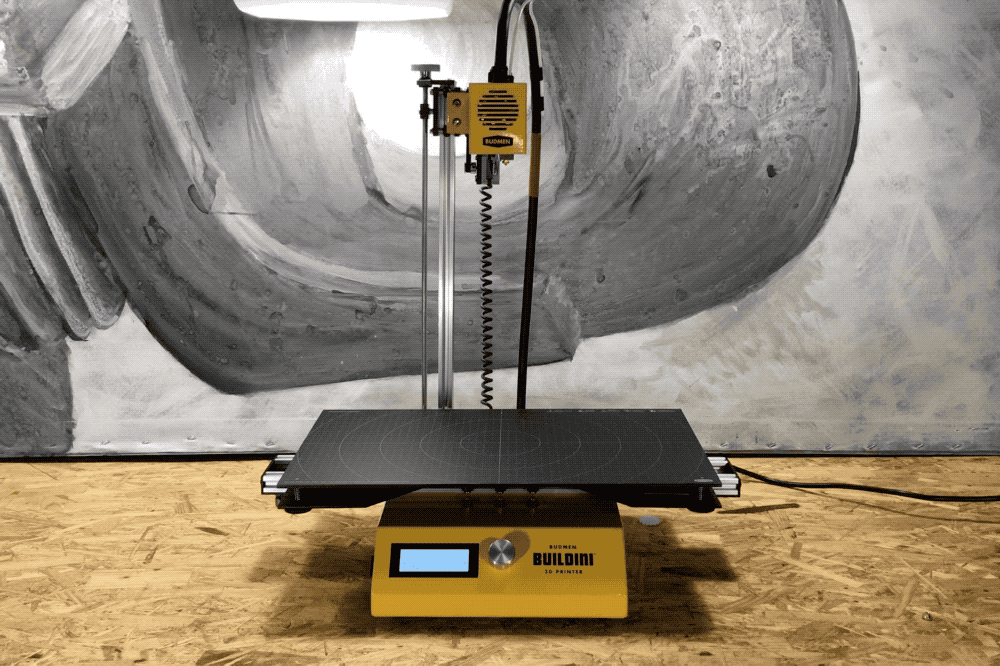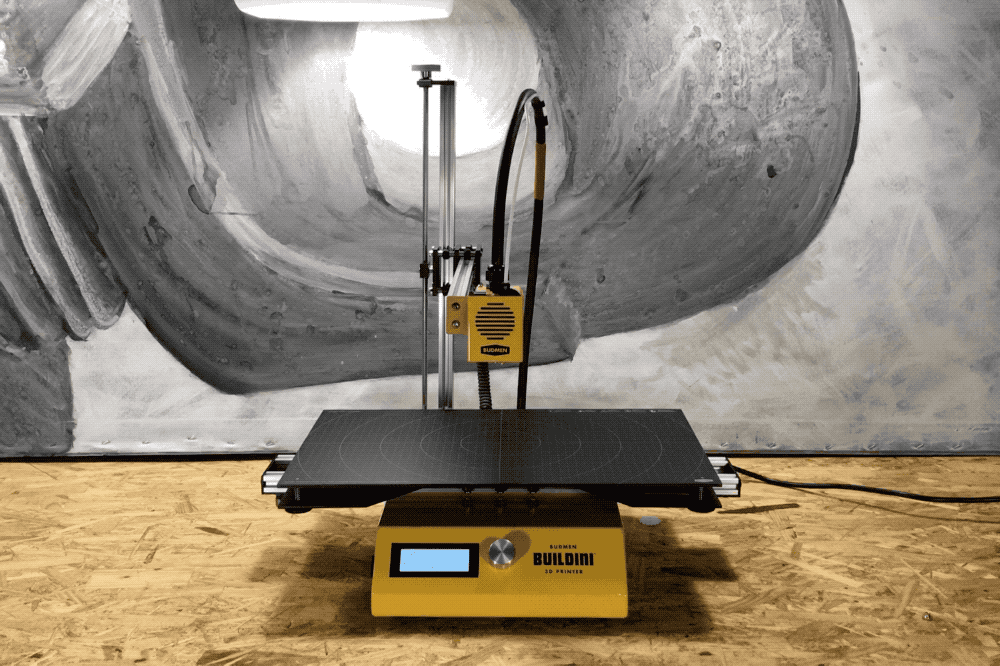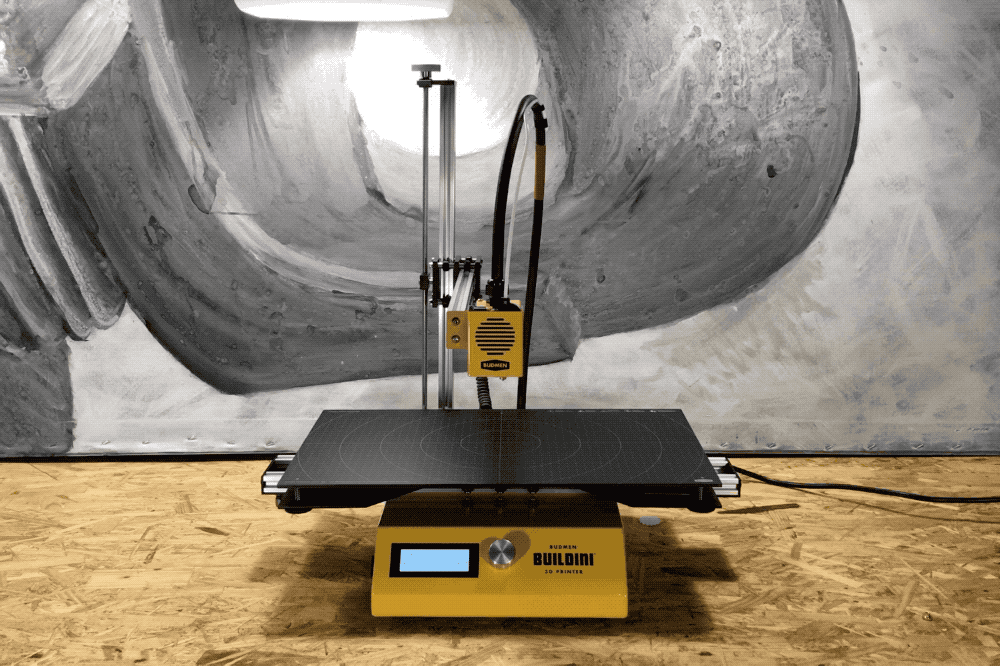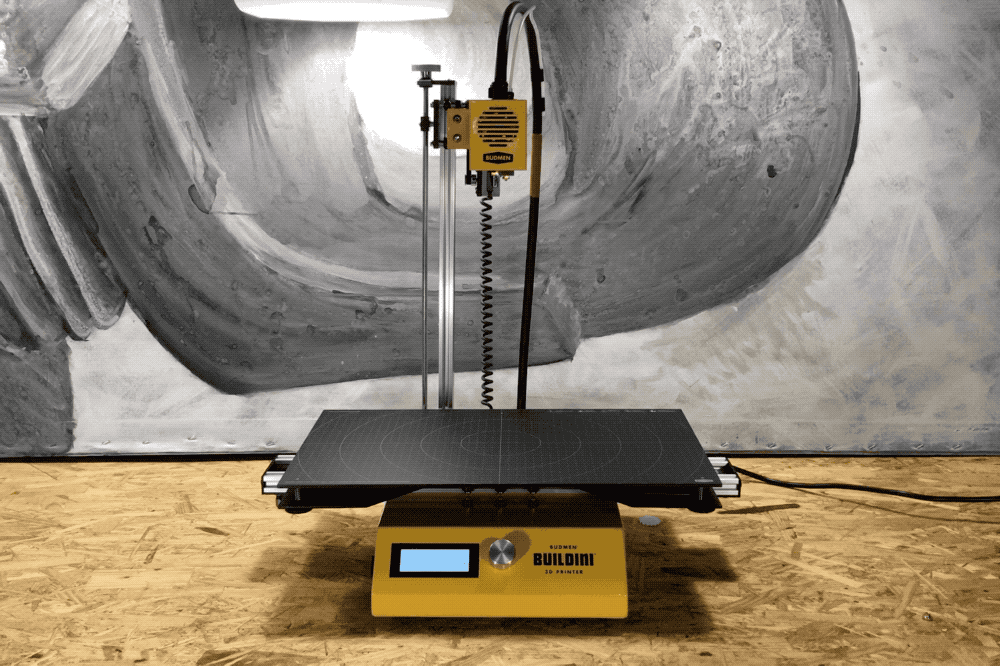 A demonstration of the Z-Axis range of motion.
A demonstration of the Z-Axis range of motion.
The final dimension on the Buildini™ 3D Printer is the Z-Axis. The motion along the Z-Axis creates the up and down motion of the extruder relative to the build platform. The Z-Axis lifts the whole Y-Axis assembly to build layer on top of layer.
Click here to go to Lesson 3: Making Things for 3D Printing
Vocab Words
- Build Platform: The surface where an object is 3D printed. Also called build plate or bed.
- Carriage: Moving assembly that travels along an axis.
- Drive Gear: Located inside the extruder, this gear is used to pull filament into the hot end.
- Extruder: Part of a 3D printer that expels plastic to deposit it in successive layers within 3D printing.
- Guide Tube: Hollow cylinder used to guide the filament accurately into the extruder.
- Filament: Thread-like plastic used to 3D print objects
- Hot End: Part of the extruder that heats filament to its melting point.
- X-Axis: Mechanical assembly that creates the left to right motion of the build platform.
- Y-Axis: Mechanical assembly that creates the front to back motion of the extruder relative to the build platform.
- Z-Axis: Mechanical assembly that creates the up and down motion of the extruder relative to the build platform.
